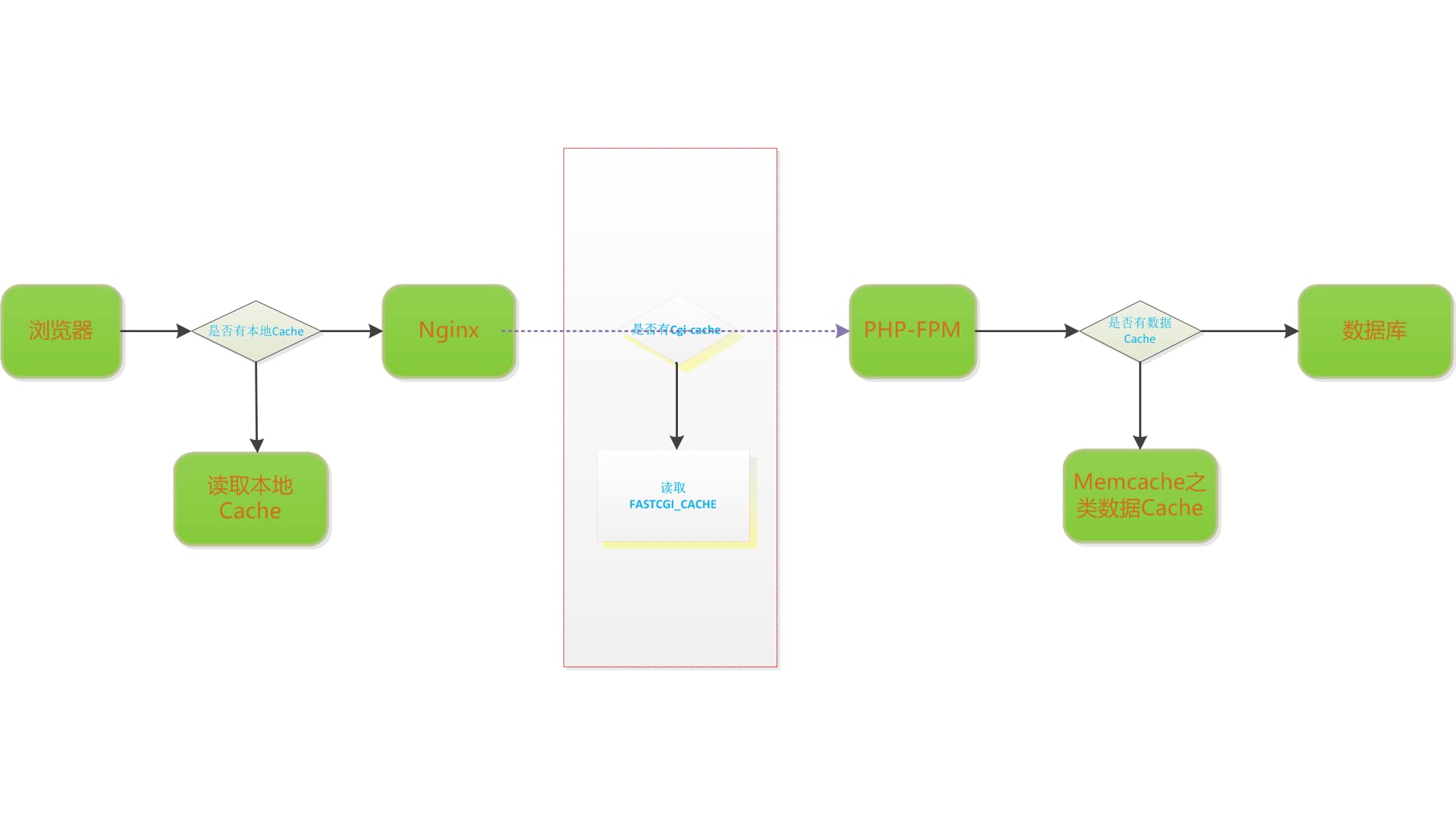
在web项目中,大家都已经非常熟悉其架构流程了。都说Cache是万金油,哪里不舒服抹哪里。这些流程中,几乎每个环节都会进行cache。从浏览器到webserver,到cgi程序,到DB数据库,会进行浏览器cache,数据cache,SQL查询的cache等等。对于fastcgi这里的cache,很少被使用。去年年底,我对nginx的fastcgi_cache 进行摸索使用。在我的测试过程中,发现一些WIKI以及网络上没被提到的注意点,这里分享一下。
这里是我的NGinx配置信息
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 add_header X-Cache-CFC "$upstream_cache_status - $upstream_response_time " ; fastcgi_temp_path /dev/shm/nginx_tmp; fastcgi_cache_path /dev/shm/nginx_cache levels=1 :2 keys_zone=cfcache:10m inactive=50m ; fastcgi_cache_key "$request_method ://$host $request_uri " ; fastcgi_cache_methods GET HEAD; fastcgi_cache cfcache; fastcgi_cache_valid any 1d ; fastcgi_cache_min_uses 1 ; fastcgi_cache_use_stale error timeout invalid_header http_500; fastcgi_ignore_client_abort on ;
配置这些参数时,注意每个参数的作用域,像fastcgi_cache_path参数,只能在http配置项里配置,而fastcgi_cache_min_uses这个参数,可以在http、server、location三个配置项里配置。这样更灵活的会每个域名、每个匹配的location进行选择性cache了。具体的参数作用域,参考FASTCGI模块的官方WIKI 。我为了调试方便,添加了一个『X-Cache-CFC』的http响应头,$upstream_cache_status 变量表示此请求响应来自cache的状态,分别为:
MISS 未命中
EXPIRED – expired, request was passed to backend Cache已过期
UPDATING – expired, stale response was used due to proxy/fastcgi_cache_use_stale updating Cache已过期,(被其他nginx子进程)更新中
STALE – expired, stale response was used due to proxy/fastcgi_cache_use_stale Cache已过期,响应数据不合法,被污染
HIT 命中cache
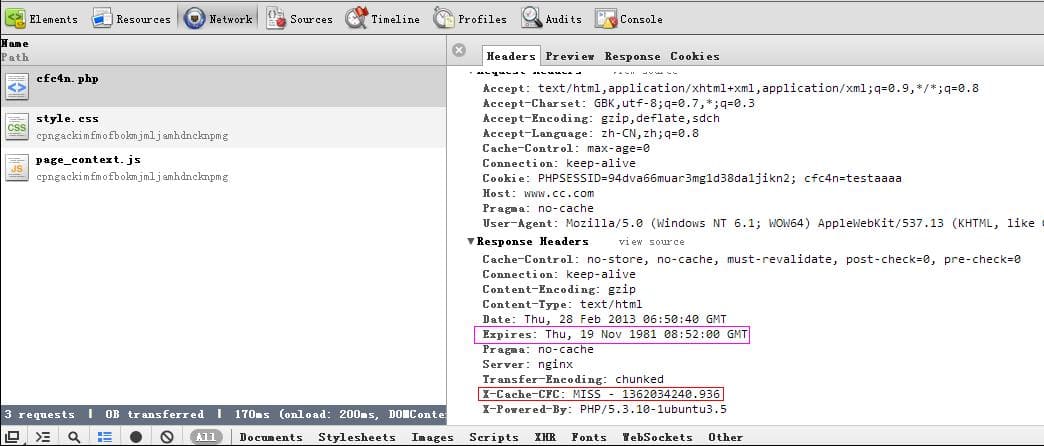
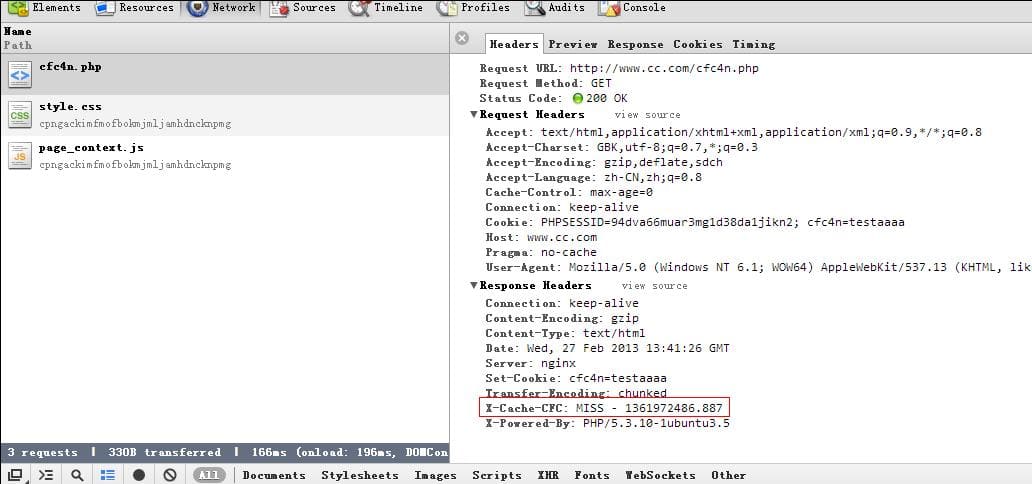
FASTCGI_CACHE $upstream_cache_status 结果为miss,一次也没命中
程序代码是Discuz!论坛, 随便开启测试了几下,发现/dev/shm/nginx_cache/下没有任何目录建立,也没有文件创建。调试的http header响应头里的X-Cache-CFC 结果一直是MISS。从服务器进程上来看,Nginx cache manager process 跟Nginx cache loader process 进程也正常运行:
1 2 3 4 root 3100 1 0 14 :52 ? 00 :00 :00 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx www -data 3101 3100 0 14 :52 ? 00 :00 :00 nginx: worker process www -data 3102 3100 0 14 :52 ? 00 :00 :00 nginx: cache manager process www -data 3103 3100 0 14 :52 ? 00 :00 :00 nginx: cache loader process
不知道为何会这样,为何没有cache成功,我以为我配置参数有问题,只好阅读WIKI。发现fastcgi_ignore_headers 参数下解释有这么一段
fastcgi_ignore_headers
也就是说这个参数的值,将会被忽略掉,同样被忽略掉的响应头比如”X-Accel-Redirect”, “X-Accel-Expires”, “Expires” or “Cache-Control”,而nginx配置中并没有fastcgi_ignore_headers参数的设定,那么问题会不会出现在FASTCGI响应结果里包含了类似”X-Accel-Redirect”, “X-Accel-Expires”, “Expires” or “Cache-Control”这几个响应头呢?用strace抓包,看了下nginx与fpm进程通讯的数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 ####为了确保准确抓到处理该http请求的进程,我把nginx 、 fpm都只开启了一个进程处理。 14 :52 :07.837334 write(3 , "\1\6\0 \1\0 \343\5\0 X-Powered-By: PHP/5.3.10-1ubuntu3.5\r \n Expires: Thu, 19 Nov 1981 08:52:00 GMT\r \n Cache-Control: no-store, no-cache, must-revalidate, post-check=0, pre-check=0\r \n Pragma: no-cache\r \n Content-type: text/html\r \n \r \n Hello cfc4n1362034327\0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \1\3\0 \1\0 \10\0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0 " , 256 ) = 256 15 :05 :13.265663 recvfrom(12 , "\1\6\0 \1\0 \343\5\0 X-Powered-By: PHP/5.3.10-1ubuntu3.5\r \n Expires: Thu, 19 Nov 1981 08:52:00 GMT\r \n Cache-Control: no-store, no-cache, must-revalidate, post-check=0, pre-check=0\r \n Pragma: no-cache\r \n Content-type: text/html\r \n \r \n Hello cfc4n1362035113\0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \1\3\0 \1\0 \10\0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0 \0 " , 4023 , 0 , NULL , NULL ) = 256
从抓取的数据包里可以看到,fpm确实返回了包含“Expires”、“Cache-Control”头的http 响应头信息。那么疑问来了:
nginx的fastcgi_cache没缓存这条http响应,是因为响应头里包含“Expires”、“Cache-Control”的原因吗?
程序里并没有输出“Expires”、“Cache-Control” http header的代码,这是谁输出的呢?
既然是fpm响应的时候,就已经有了,那么是php的core模块,还是其他拓展模块输出的?
“Expires:”时间为何是“Thu, 19 Nov 1981 08:52:00 GMT”?
疑问比较多,一个一个查起,先从Nginx的fastcgi_cache没缓存这条http响应查起。我根据测试环境nginx版本1.1.9(ubuntu 12.04默认的),到nginx官方下了对应版本的源码,搜索了fastcgi参数使用的地方,在http\ngx_http_upstream.c找到了。虽然不能很流程的读懂nginx的代码,但粗略的了解,根据了解的情况加以猜测,再动手测试实验,也得出了结论,确定了nginx的fastcgi_cache的规则。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 static ngx_int_t ngx_http_upstream_process_set_cookie(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_table_elt_t *h, ngx_uint_t offset) { #if (NGX_HTTP_CACHE) ngx_http_upstream_t *u; u = r-> if (!(u->conf -> u ->0 ; } #endif return NGX_OK; } static ngx_int_t ngx_http_upstream_process_expires(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_table_elt_t *h, ngx_uint_t offset) { ngx_http_upstream_t *u; u = r-> u -> #if (NGX_HTTP_CACHE) { time_t expires; if (u->conf -> return NGX_OK; } if (r-> return NGX_OK; } if (r->cache ->0 ) { return NGX_OK; } expires = ngx_http_parse_time(h->value .data , h-> if (expires == NGX_ERROR || expires < ngx_time()) { u->0 ; return NGX_OK; } r ->cache -> } #endif return NGX_OK; } if (ngx_strlcasestrn(p, last, (u_char *) "no-cache" , 8 - 1 ) != NULL || ngx_strlcasestrn(p, last, (u_char *) "no-store" , 8 - 1 ) != NULL || ngx_strlcasestrn(p, last, (u_char *) "private" , 7 - 1 ) != NULL) { u ->0 ; return NGX_OK; } p = ngx_strlcasestrn(p, last, (u_char *) "max-age=" , 8 - 1 ); if (p == NULL) { return NGX_OK; } ... r ->cache ->
也就是说,fastcgi响应http请求的结果中,响应头包括Expires、Cache-Control、Set-Cookie三个,都会可能不被cache,但不只有这些,别忘了nginx配置中fastcgi_ignore_headers参数设定的部分。以及ngxin的X-ACCEL X-Accel-Redirect、X-Accel-Expires、X-Accel-Charset、X-Accel-Buffering等nginx自定义的响应头。由于这几个不常用,我也没深入研究。通过对nginx的ngx_http_upstream模块代码模糊理解,加猜测,以及写了脚本测试验证,可以得到结论是正确的。即Nginx fastcgi_cache在缓存后端fastcgi响应时,当响应里包含“set-cookie”时,不缓存;当响应头包含Expires时,如果过期时间大于当前服务器时间,则nginx_cache会缓存该响应,否则,则不缓存;当响应头包含Cache-Control时,如果Cache-Control参数值为no-cache、no-store、private中任意一个时,则不缓存,如果Cache-Control参数值为max-age时,会被缓存,且nginx设置的cache的过期时间,就是系统当前时间 + mag-age的值。
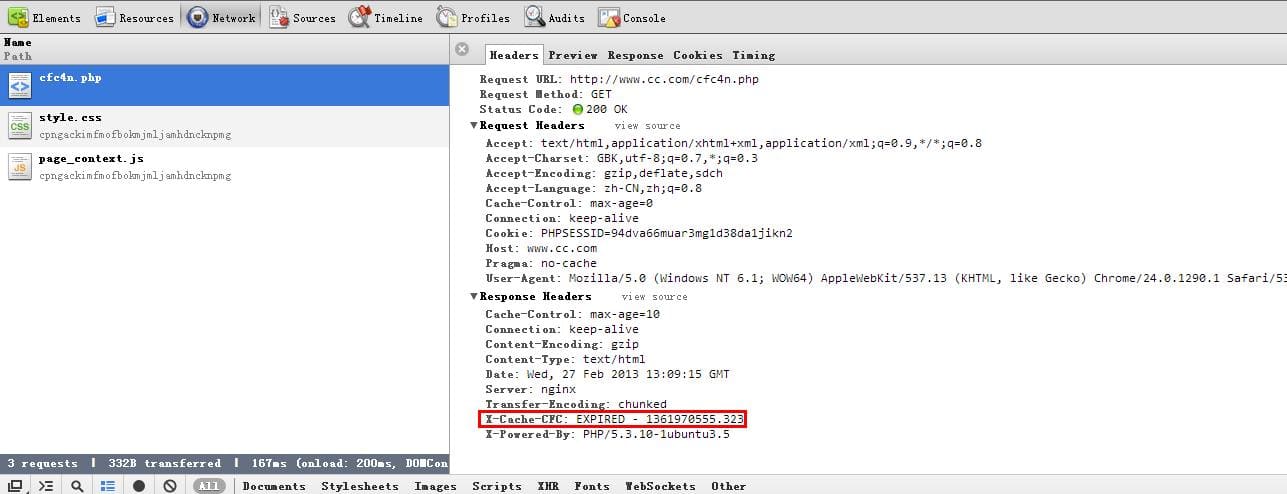
nginx fastcgi_cache 响应expired
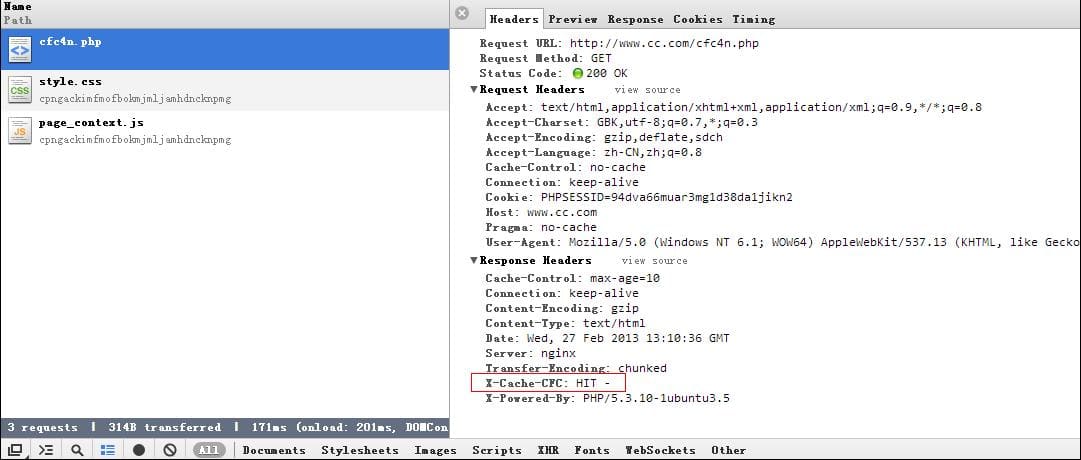
nginx fastcgi_cache hit命中
FASTCGI_CACHE $upstream_cache_status 结果为miss,一次也没命中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 //逐个测试,测试时,注释其他的 header ("Expires: ".gmdate("D, d M Y H:i:s", time ()+10000 ).' GMT' ); header ("Expires: ".gmdate("D, d M Y H:i:s", time ()-99999 ).' GMT' ); header ("X-Accel-Expires:30"); header ("Cache-Control: no-cache"); header ("Cache-Control: no-store"); header ("Cache-Control: private"); header ("Cache-Control: max-age=10"); setcookie('cfc4n' ,"testaaaa"); echo 'Hello cfc4n' ,time ();
到了这里,疑问1解决了。那么疑问2、3呢?程序里并没有输出“Expires”、“Cache-Control” http header的代码,这是谁输出的呢?既然是fpm响应的时候,就已经有了,那么是php的core模块,还是其他拓展模块输出的?我精简了代码,只输出一个“hello world”,发现也确实被缓存了。显然,php脚本程序中并没输出http header 的“Expires”、“Cache-Control”,多次测试,最终定位到session_start函数,翻阅源码找到了这些代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 CACHE_LIMITER_FUNC(private ) { ADD_HEADER("Expires: Thu, 19 Nov 1981 08:52:00 GMT" ) ; CACHE_LIMITER(private_no_expire ) (TSRMLS_C); } CACHE_LIMITER_FUNC(nocache ) { ADD_HEADER("Expires: Thu, 19 Nov 1981 08:52:00 GMT" ) ; ADD_HEADER("Cache-Control: no-store, no-cache, must-revalidate, post-check=0, pre-check=0" ) ; ADD_HEADER("Pragma: no-cache" ) ; } static php_session_cache_limiter_t php_session_cache_limiters[] = { CACHE_LIMITER_ENTRY(public ) CACHE_LIMITER_ENTRY(private ) CACHE_LIMITER_ENTRY(private_no_expire ) CACHE_LIMITER_ENTRY(nocache ) {0 } }; static int php_session_cache_limiter(TSRMLS_D) { php_session_cache_limiter_t *lim; if (PS(cache_limiter ) [0 ] == '\0' ) return 0 ; if (SG(headers_sent ) ) { const char *output_start_filename = php_output_get_start_filename(TSRMLS_C) ; int output_start_lineno = php_output_get_start_lineno(TSRMLS_C) ; if (output_start_filename) { php_error_docref(NULL TSRMLS_CC, E_WARNING, "Cannot send session cache limiter - headers already sent (output started at %s:%d)" , output_start_filename , output_start_lineno ) ; } else { php_error_docref(NULL TSRMLS_CC, E_WARNING, "Cannot send session cache limiter - headers already sent" ) ; } return -2 ; } for (lim = php_session_cache_limiters; lim->name; lim++) { if (!strcasecmp(lim->name, PS(cache_limiter ) )) { lim->func(TSRMLS_C); return 0 ; } } return -1 ; }
到了这里,知道原因了,是程序调用session_start时,php的session拓展自己输出的。session.cache_limit参数来决定输出包含哪种Expires的header,默认是nocache,修改php.ini的session.cache_limit参数为“none”即可让session模块不再输出这些http 响应头。或在调用session_start之前,使用session_cache_limiter函数来指定下该参数值。那为什么要在使用session时,发Expires、Cache-Control的http response header呢?我猜测了下,需要session时,基本上是用户跟服务器有交互,那么,既然有交互,就意味着用户的每次交互结果也可能不一样,就不能cache这个请求的结果,给返回给这个用户。同时,每个用户的交互结果都是不一样的,nginx也就不能把包含特殊Cache-Control的个人响应cache给其他人提供了。
还有一个无聊的问题“Expires:时间为何是Thu, 19 Nov 1981 08:52:00 GMT”?我翻阅了session.c这段代码的添加时间,版本,作者信息,在php官方版本库中找到了这次提交的信息 :
1 2 3 4 5 6 Revision 17092 – (view) (download) (as text) (annotate) – [select for diffs] Modified Sun Dec 12 14 :16 :55 1999 UTC (13 years, 2 months ago) by sasFile length: 28327 byte(s)Diff to previous 16964 Add cache_limiter and cache_expire options. Rename extern_referer_checkto referer_check.
对比session.c两个版本 的变更,果然是这块代码。作者是sas,也就是Sascha Schumann, http://php.net/credits.php 里可以看到他的大名。关于这个expires过期时间的问题,有人在stackoverflow也提问过,Why is “Expires” 1981? ,别人说那天是他生日。这是真的么?如果那天是他生日的话,而他增加session.cache_limiter时是1999年,他才17岁,17岁呀。我17岁时在干嘛?还不知道电脑长啥样,正在玩『超级玛丽』呢。
好奇的不是我一个人,还有个帖子是epoch date — Expires: Thu, 19 Nov 1981 08:52:00 也问了。另外两个地址虽然没问,也有人提到那天是他生日了。http://boinc.berkeley.edu/dev/forum_thread.php?id=2514 、https://github.com/codeguy/Slim/issues/157 ,这些帖子都提到说原帖是http://www.phpbuilder.com/lists/php3-list/199911/3159.php ,我无法访问,被跳转到首页了。用http://web.archive.org 找到了历史快照 ,发现上下文关系不大,也不能证明是他生日。 我更是好奇的发了两封邮件到他的不同邮箱里问他,不过,目前他还没回复。或许他没收到、没看到,或许懒得回了。N年后,“Expires:时间为何是Thu, 19 Nov 1981 08:52:00 GMT”这个日期,会不会又成了一段奇闻佳话了呢?