一、ListFragement的介绍: ListFragment继承于Fragment。因此它具有Fragment的特性,能够作为activity中的一部分,目的也是为了使页面设计更加灵活。相比Fragment,ListFragment的内容是以列表(list)的形式显示的。
1、ListFragment布局:
ListFragment的默认布局包含一个list view。因此,在ListFragment对应的布局文件中,必须指定一个 android:id 为 “@android:id/list” 的ListView控件! 若用户想修改listview,可以在onCreateView(LayoutInflater, ViewGroup, Bundle)中进行修改。当然,用户也可以在ListFragment的布局中包含其它的控件。
下面是官方文档中ListFragment对应的一个layout示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android ="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation ="vertical" android:layout_width ="match_parent" android:layout_height ="match_parent" android:paddingLeft ="8dp" android:paddingRight ="8dp" > <ListView android:id ="@id/android:list" android:layout_width ="match_parent" android:layout_height ="match_parent" android:background ="#00FF00" android:layout_weight ="1" android:drawSelectorOnTop ="false" /> <TextView android:id ="@id/android:empty" android:layout_width ="match_parent" android:layout_height ="match_parent" android:background ="#FF0000" android:text ="No data" /> </LinearLayout >
ListView中每一行的显示内容,是通过设置适配器ListAdapter来实现的。我们既可以自定义,也可以采用系统默认的layout。后面的应用实例中,会分别列举2种情况下的显示
2、绑定数据:
ListFragment绑定ListView的数据(即绑定适配器)时,必须通过ListFragment.setListAdapter()接口来绑定数据,而不是使用ListView.setAdapter() 或其它方法
二、通过ArrayAdapter来加载ListFragment的举例: 【举例】现在将平板电脑分成三部分:点击左侧的按钮,出现中间的新闻标题列表(ListFragment),点击中间ListFragment的某个item,在最右侧的fragment中显示详情。
新建工程文件m01_ListFragment01:
(1)定义activity_main.xml的布局:
activity_main.xml的代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 <LinearLayout xmlns:android ="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools ="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width ="match_parent" android:layout_height ="match_parent" tools:context =".MainActivity" > <LinearLayout android:id ="@+id/left" android:layout_width ="0dp" android:layout_height ="match_parent" android:layout_weight ="1" android:background ="#cccccc" android:orientation ="horizontal" > <Button android:id ="@+id/button1" android:layout_width ="match_parent" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:textSize ="14sp" android:text ="show ListFragment" /> </LinearLayout > <LinearLayout android:id ="@+id/center" android:layout_width ="0dp" android:layout_height ="match_parent" android:layout_weight ="2" android:background ="#AFEEEE" android:orientation ="vertical" > </LinearLayout > <LinearLayout android:id ="@+id/center" android:layout_width ="0dp" android:layout_height ="match_parent" android:layout_weight ="2" android:background ="#00FFFF" android:orientation ="vertical" > </LinearLayout > </LinearLayout >
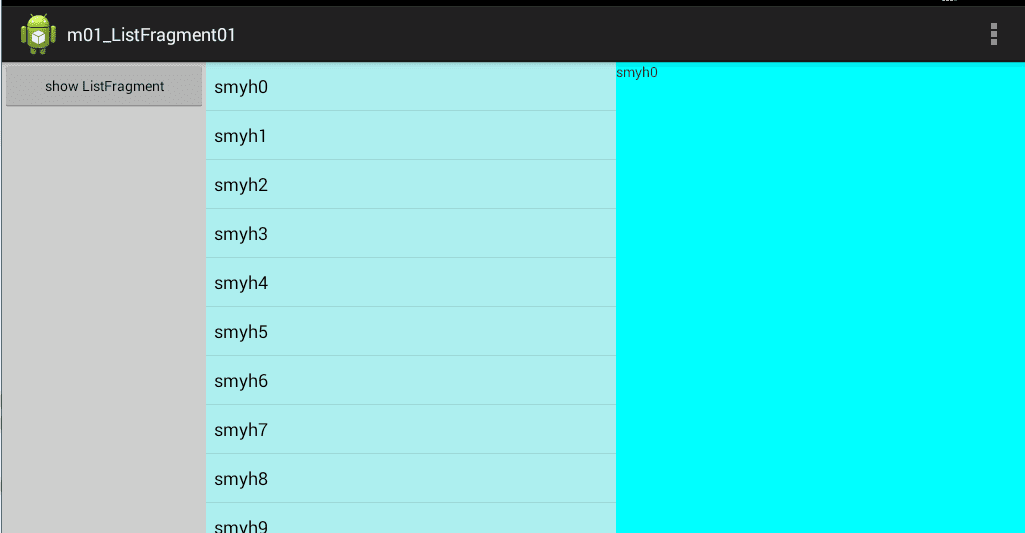
实际上分配了三个线性布局,左侧显示按钮,中间显示标题,右侧显示详情。这个布局文件对应的可视化界面如下:
ArticleListFragment.java的代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 package com.example.m01_listfragment01;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;import android.app.ListFragment;import android.os.Bundle;import android.view.LayoutInflater;import android.view.View;import android.view.ViewGroup;import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;public class ArticleListFragment extends ListFragment { private ArrayAdapter<String> adapter; @Override public void onCreate (Bundle savedInstanceState) { super .onCreate(savedInstanceState); List<String> data = new ArrayList <String>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < 30 ; i++) { data.add("smyh" + i); } adapter = new ArrayAdapter <String>(getActivity(), android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, data); setListAdapter(adapter); } @Override public View onCreateView (LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) { return super .onCreateView(inflater, container, savedInstanceState); } @Override public void onPause () { super .onPause(); } }
核心代码是22至32行:我们让这个Fragment继承ListFragment,然后在onCreate()方法中定义一个ArrayAdapter,将数据放进去,最后绑定适配器就行了。需要注意的是,由于我们继承的是ListFragment,这个Fragment默认自带了一个布局,所以我们不需要重新新建布局文件了。
(3)将中间的ListFragment加载到Activity当中去。当我们点击按钮时,就开始加载这个Fragment:
MainActivity.java的代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 package com.example.m01_listfragment01;import android.app.Activity;import android.app.FragmentManager;import android.app.FragmentTransaction;import android.os.Bundle;import android.view.Menu;import android.view.View;import android.view.View.OnClickListener;import android.widget.Button;public class MainActivity extends Activity { private FragmentManager manager; private FragmentTransaction transaction; @Override protected void onCreate (Bundle savedInstanceState) { super .onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); Button button = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button1); button.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener () { @Override public void onClick (View v) { manager = getFragmentManager(); transaction = manager.beginTransaction(); ArticleListFragment articleListFragment = new ArticleListFragment (); transaction.add(R.id.center, articleListFragment, "article" ); transaction.commit(); } }); } @Override public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu (Menu menu) { getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu); return true ; } }
这个代码比较简单,就不多解释了。
现在运行程序,初始界面如下:
(代码放置的位置是:让它和Fragment的生命周期方法并列就行了)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @Override public void onListItemClick(ListView l , View v , int position , long id ) { super.onListItemClick(l , v , position , id ) ; String item = adapter.getItem(position ) ; Toast .Text(getActivity () , item, 1 ).show() ; }
由此我们可以看到,监听事件的函数为onListItemClick(),可以直接写,不需要set。
这里面关键代码在第05行,通过getItem()接收那个item,然后用字符串来接收。
我们先去掉这部分的监听事件代码,继续往下看。
(4)点击中间ListFragment的item,加载右边的DetailFragment:
我们在中间ListFragment中添加一个按钮的监听事件,监听事件的函数为onListItemClick(),ArticleListFragment.java在上面代码的基础之上,添加的代码如下:
(代码放置的位置是:让它和Fragment的生命周期方法并列就行了)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 @Override public void onListItemClick(ListView l , View v , int position , long id ) { super.onListItemClick(l , v , position , id ) ; FragmentManager manager = getFragmentManager() ; FragmentTransaction transaction = manager.begin Transaction() ; DetailFragment detailFragment = new DetailFragment() ; transaction.replace(R ."detailFragment" ); String item = adapter.getItem(position ) ; Bundle args = new Bundle() ; args.putString("item" ,item ) ; detailFragment.setArguments(args ) ; transaction.commit() ; }
上面的代码中,我们是在中间的Fragment中点击按钮,然后加载右边的Fragment,然后要注意14至18行的核心代码,看一下它是如何通过bundle来传递数据的。
需要注意的是,第12行代码必须用replace的方式加载右侧的fragment,而不是add;如果用add,运行的错误稍后将展示出来。
(5)定义右边的DetailFragment:
先定义布局文件,在里面加一个TextView,fragment_detail.xml的代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android ="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width ="match_parent" android:layout_height ="match_parent" android:orientation ="vertical" > <TextView android:id ="@+id/textView1" android:layout_width ="wrap_content" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:text ="TextView" /> </LinearLayout >
然后新建文件,DetailFragment.java的代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 package com.example.m01_listfragment01;import android.app.Fragment;import android.os.Bundle;import android.view.LayoutInflater;import android.view.View;import android.view.ViewGroup;import android.widget.TextView;public class DetailFragment extends Fragment { @Override public void onCreate (Bundle savedInstanceState) { super .onCreate(savedInstanceState); } @Override public View onCreateView (LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) { View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_detail, null ); TextView textView = (TextView)view.findViewById(R.id.textView1); textView.setText("" +getArguments().getString("item" )); return view; } @Override public void onPause () { super .onPause(); } }
核心代码是第25行,仔细看一下我们是怎么通过键值对来拿到中间的Fragment传递过来的item的内容。
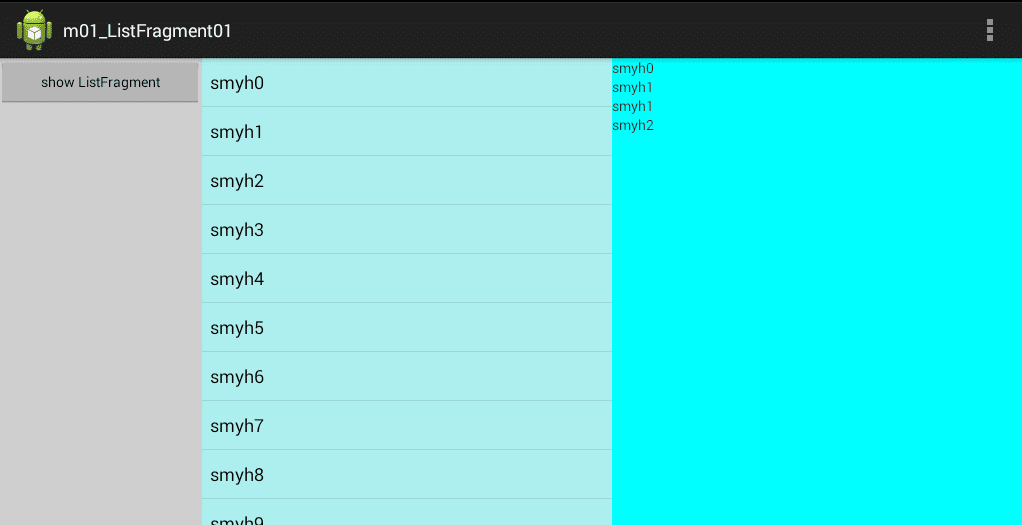
现在运行程序,一次点击左边的按钮和中间的item,效果如下:
【声明】
欢迎转载,但请保留文章原始出处→_→
生命壹号:http://www.cnblogs.com/smyhvae/
文章来源:http://www.cnblogs.com/smyhvae/p/4000483.html
联系方式:smyhvae@163.com