前言:这段时间感觉自己也有点懒了,真是内心有点自责呢,除了工作,也没做点什么,EventBus也是一周前总结出来的,只能以写博客为名来弥补内心的罪恶感了,集合同事们做的项目,虽然上周开动了,但总感觉大家积极性不高,如何才能做一个合格的管理者,还真是一个考验。follow your heart!! just do it!
一、概述 前一篇给大家装简单演示了EventBus的onEventMainThread()函数的接收,其实EventBus还有另外有个不同的函数,他们分别是:
1、onEvent
这四种订阅函数都是使用onEvent开头的,它们的功能稍有不同,在介绍不同之前先介绍两个概念:
onEvent:如果使用onEvent作为订阅函数,那么该事件在哪个线程发布出来的,onEvent就会在这个线程中运行,也就是说发布事件和接收事件线程在同一个线程。使用这个方法时,在onEvent方法中不能执行耗时操作,如果执行耗时操作容易导致事件分发延迟。
onEventMainThread:如果使用onEventMainThread作为订阅函数,那么不论事件是在哪个线程中发布出来的,onEventMainThread都会在UI线程中执行,接收事件就会在UI线程中运行,这个在Android中是非常有用的,因为在Android中只能在UI线程中跟新UI,所以在onEvnetMainThread方法中是不能执行耗时操作的。
onEventBackground:如果使用onEventBackgrond作为订阅函数,那么如果事件是在UI线程中发布出来的,那么onEventBackground就会在子线程中运行,如果事件本来就是子线程中发布出来的,那么onEventBackground函数直接在该子线程中执行。
onEventAsync:使用这个函数作为订阅函数,那么无论事件在哪个线程发布,都会创建新的子线程在执行onEventAsync.
二、实战 1、解析
上面列出的这四个函数,关键问题在于,我们怎么指定调用哪个函数呢?
我们先研究一下,上一篇中是怎么调用的onEventMainThread函数,除了在接收端注册与反注册以后,关键问题在于新建的一个类:
新建一个类:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 package com.harvic.other; public class FirstEvent { private String mMsg; public FirstEvent (String msg) mMsg = msg; } public String getMsg () return mMsg; } }
发送时:
EventBus.getDefault().post(new FirstEvent("FirstEvent btn clicked"));
接收时:
1 2 3 public void onEventMainThread (FirstEvent event ) …… }
发现什么问题了没?
没错,发送时发送的是这个类的实例,接收时参数就是这个类实例。
所以!!!!!!当发过来一个消息的时候,EventBus怎么知道要调哪个函数呢,就看哪个函数传进去的参数是这个类的实例,哪个是就调哪个。那如果有两个是呢,那两个都会被调用!!!!
为了证明这个问题,下面写个例子,先看下效果
2、实例
先看看我们要实现的效果:
这次我们在上一篇的基础上,新建三个类:FirstEvent、SecondEvent、ThirdEvent,在第二个Activity中发送请求,在MainActivity中接收这三个类的实例,接收时的代码为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public void onEventMainThread (FirstEvent event ) Log.d("harvic" , "onEventMainThread收到了消息:" + event .getMsg()); } public void onEventMainThread (SecondEvent event ) Log.d("harvic" , "onEventMainThread收到了消息:" + event .getMsg()); } public void onEvent (ThirdEvent event ) Log.d("harvic" , "OnEvent收到了消息:" + event .getMsg()); }
使用两个onEventMainThread分别接收FirstEvent实例的消息和SecondEvent实例的消息,使用onEvent接收ThirdEvent实例的消息。界面操作及结果如下:
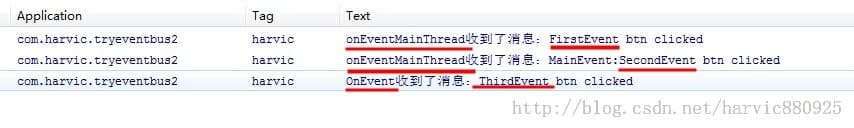
Log输出结果:
可以看到,在发送FirstEvent时,在MainActiviy中虽然有三个函数,但只有第一个onEventMainThread函数的接收参数是FirstEvent,所以会传到它这来接收。所以这里识别调用EventBus中四个函数中哪个函数,是通过参数中的实例来决定的。
因为我们是在上一篇例子的基础上完成的,所以这里的代码就不详细写了,只写改动的部分。
1、三个类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 package com.harvic.other; public class FirstEvent { private String mMsg; public FirstEvent (String msg) mMsg = msg; } public String getMsg () return mMsg; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 package com.harvic.other; public class SecondEvent { private String mMsg; public SecondEvent (String msg) mMsg = "MainEvent:" +msg; } public String getMsg () return mMsg; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 package com.harvic.other; public class ThirdEvent { private String mMsg; public ThirdEvent (String msg) mMsg = msg; } public String getMsg () return mMsg; } }
2、发送
然后在SecondActivity中新建三个按钮,分别发送不同的类的实例,代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 package com.harvic.tryeventbus2; import com.harvic.other.FirstEvent; import com.harvic.other.SecondEvent; import com.harvic.other.ThirdEvent; import de.greenrobot.event.EventBus; import android.app.Activity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.View; import android.widget.Button; public class SecondActivity extends Activity { private Button btn_FirstEvent, btn_SecondEvent, btn_ThirdEvent; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState ) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState ) ; setContentView(R.layout .activity_second ) ; btn_FirstEvent = (Button) findViewById(R.id .btn_first_event ) ; btn_SecondEvent = (Button) findViewById(R.id .btn_second_event ) ; btn_ThirdEvent = (Button) findViewById(R.id .btn_third_event ) ; btn_FirstEvent.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v ) { EventBus .Default() .post( new FirstEvent("FirstEvent btn clicked" ) ); } }); btn_SecondEvent.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v ) { EventBus .Default() .post( new SecondEvent("SecondEvent btn clicked" ) ); } }); btn_ThirdEvent.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v ) { EventBus .Default() .post( new ThirdEvent("ThirdEvent btn clicked" ) ); } }); } }
3、接收
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 package com.harvic .tryeventbus2 ; import com.harvic .other .FirstEvent ; import com.harvic .other .SecondEvent ; import com.harvic .other .ThirdEvent ; import de.greenrobot .event .EventBus ; import android.app .Activity ; import android.content .Intent ; import android.os .Bundle ; import android.util .Log ; import android.view .Menu ; import android.view .MenuItem ; import android.view .View ; import android.widget .Button ; import android.widget .TextView ; public class MainActivity extends Activity { Button btn; TextView tv; EventBus eventBus; @Override protected void onCreate (Bundle savedInstanceState ) { super .onCreate (savedInstanceState); setContentView (R.layout .activity_main ); EventBus .getDefault ().register (this ); btn = (Button ) findViewById (R.id .btn_try ); btn.setOnClickListener (new View .OnClickListener () { @Override public void onClick (View v ) { Intent intent = new Intent (getApplicationContext (), SecondActivity .class ); startActivity (intent); } }); } public void onEventMainThread (FirstEvent event ) { Log .d ("harvic" , "onEventMainThread收到了消息:" + event.getMsg ()); } public void onEventMainThread (SecondEvent event ) { Log .d ("harvic" , "onEventMainThread收到了消息:" + event.getMsg ()); } public void onEvent (ThirdEvent event ) { Log .d ("harvic" , "OnEvent收到了消息:" + event.getMsg ()); } @Override protected void onDestroy ( super .onDestroy (); EventBus .getDefault ().unregister (this ); } }
到这里,代码就结束 了,从上面的代码,我们可以看到,EventBus是怎么接收消息的,是根据参数中类的实例的类型的判定的,所以当如果我们在接收时,同一个类的实例参数有两个函数来接收会怎样?答案是,这两个函数都会执行,下面实验一下:
在MainActivity中接收时,我们在接收SecondEvent时,在上面onEventMainThread基础上另加一个onEventBackgroundThread和onEventAsync,即下面的代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public void onEventMainThread (SecondEvent event ) Log.d("harvic" , "onEventMainThread收到了消息:" + event .getMsg()); } public void onEventBackgroundThread (SecondEvent event ) Log.d("harvic" , "onEventBackground收到了消息:" + event .getMsg()); } public void onEventAsync (SecondEvent event ) Log.d("harvic" , "onEventAsync收到了消息:" + event .getMsg()); }
完整的代码在这里:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 package com.harvic .tryeventbus2 ; import com.harvic .other .FirstEvent ; import com.harvic .other .SecondEvent ; import com.harvic .other .ThirdEvent ; import de.greenrobot .event .EventBus ; import android.app .Activity ; import android.content .Intent ; import android.os .Bundle ; import android.util .Log ; import android.view .Menu ; import android.view .MenuItem ; import android.view .View ; import android.widget .Button ; import android.widget .TextView ; public class MainActivity extends Activity { Button btn; TextView tv; EventBus eventBus; @Override protected void onCreate (Bundle savedInstanceState ) { super .onCreate (savedInstanceState); setContentView (R.layout .activity_main ); EventBus .getDefault ().register (this ); btn = (Button ) findViewById (R.id .btn_try ); btn.setOnClickListener (new View .OnClickListener () { @Override public void onClick (View v ) { Intent intent = new Intent (getApplicationContext (), SecondActivity .class ); startActivity (intent); } }); } public void onEventMainThread (FirstEvent event ) { Log .d ("harvic" , "onEventMainThread收到了消息:" + event.getMsg ()); } public void onEventMainThread (SecondEvent event ) { Log .d ("harvic" , "onEventMainThread收到了消息:" + event.getMsg ()); } public void onEventBackgroundThread (SecondEvent event ){ Log .d ("harvic" , "onEventBackground收到了消息:" + event.getMsg ()); } public void onEventAsync (SecondEvent event ){ Log .d ("harvic" , "onEventAsync收到了消息:" + event.getMsg ()); } public void onEvent (ThirdEvent event ) { Log .d ("harvic" , "OnEvent收到了消息:" + event.getMsg ()); } @Override protected void onDestroy ( super .onDestroy (); EventBus .getDefault ().unregister (this ); } }
经过上面的分析,当发送SecondEvent实例的消息过来的时候,这三个函数会同时接收到并各自执行,所以当点击Second Event这个button的时候,会出现下面的结果:
好啦,这篇就到了,讲来讲去就是说一个问题:消息的接收是根据参数中的类名来决定执行哪一个的。
如果我的文章有帮到你,记得关注哦!
源码下载地址:http://download.csdn.net/detail/harvic880925/8128633
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/harvic880925/article/details/40787203 《Android解耦库EventBus的使用和源码分析》 《EventBus的使用初试》 《EventBusExplained 》 《Google Guava EventBus实例与分析》