在Android程序开发中,我们经常会去用到Shape这个东西去定义各种各样的形状,首先我们了解一下Shape下面有哪些标签,都代表什么意思:
solid:填充
android:color指定填充的颜色
gradient:渐变
android:startColor和android:endColor分别为起始和结束颜色,
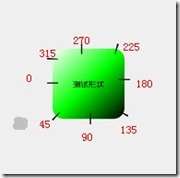
android:angle是渐变角度,必须为45的整数倍。
另外渐变默认的模式为android:type="linear",即线性渐变,
可以指定渐变为径向渐变,android:type="radial",径向渐变需要指定半径android:gradientRadius="50"。
angle值对应的位置如图:
stroke:描边
android:width 描边的宽度,android:color 描边的颜色。
我们还可以把描边弄成虚线的形式,设置方式为:
android:dashWidth="5dp"
android:dashGap="3dp"
其中android:dashWidth表示’-‘这样一个横线的宽度,android:dashGap表示之间隔开的距离
corners:圆角
android:radius为角的弧度,值越大角越圆。
我们还可以把四个角设定成不同的角度,
同时设置五个属性,则Radius属性无效
- android:Radius=”20dp” 设置四个角的半径
- android:topLeftRadius=”20dp” 设置左上角的半径
- android:topRightRadius=”20dp” 设置右上角的半径
- android:bottomLeftRadius=”20dp” 设置右下角的半径
- android:bottomRightRadius=”20dp” 设置左下角的半径
padding:间隔
可以设置上下左右四个方向的间隔
在这里我们来看一个简单的小例子,ShapDemo,在drawable文件夹下面先定义两个xml文件:
button_bg.xml的内容如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" >
<solid android:color="#ff9d77" />
<size
android:width="50dp"
android:height="50dp"/>
<stroke
android:width="2dp"
android:color="#fad3cf" />
<corners
android:bottomLeftRadius="5dp"
android:bottomRightRadius="5dp"
android:topLeftRadius="5dp"
android:topRightRadius="5dp" />
<padding
android:bottom="10dp"
android:left="10dp"
android:right="10dp"
android:top="10dp" />
</shape>
|
button_pressed_bg.xml的内容如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" >
<gradient
android:endColor="#FFFFFF"
android:gradientRadius="50"
android:startColor="#ff8c00"
android:type="radial" />
<stroke
android:dashGap="3dp"
android:dashWidth="5dp"
android:width="2dp"
android:color="#dcdcdc" />
<corners android:radius="5dp" />
<padding
android:bottom="10dp"
android:left="10dp"
android:right="10dp"
android:top="10dp" />
</shape>
|
这里说明一点,在描边里面设置了dash参数,使得图形的边变成了虚线
在drawable文件夹下添加一个button.xml文件,内容如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item android:drawable="@drawable/button_pressed_bg" android:state_pressed="true"></item>
<item android:drawable="@drawable/button_bg"></item>
</selector>
|
这个文件的意思以前讲过,normal(正常)情况下就显示button_bg,被press(按下)情况下就显示button_pressed_bg。
我们再来看一下layout目录下的activity_main.xml的内容:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@drawable/button"
android:text="TestShapeButton" />
</RelativeLayout>
|
直接将background指定为drawable文件夹下的button.xml。
程序运行截图如下:

附上例子工程源码:
Android中使用shape自定义形状
自由的边框
当前版本的Android SDK并没有给stroke提供bottom、left、right之类的属性,也就是说你无法通过它来让长方形的边框少于4条。啊,真是太遗憾了。怎么办呢?有人想到了对Layer List hack。 在StackOverflow上有不少这样的把戏。
为了实现只有left,right和top边框,我们可以这么写:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<layer-list xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" >
<item>
<shape android:shape="rectangle" >
<stroke
android:width="1dp"
android:color="@color/card_stroke" />
</shape>
</item>
<item
android:left="2dp"
android:right="2dp"
android:top="2dp">
<shape android:shape="rectangle" >
<solid android:color="@color/solid_white" />
</shape>
</item>
</layer-list>
|
原理差不多是这样:
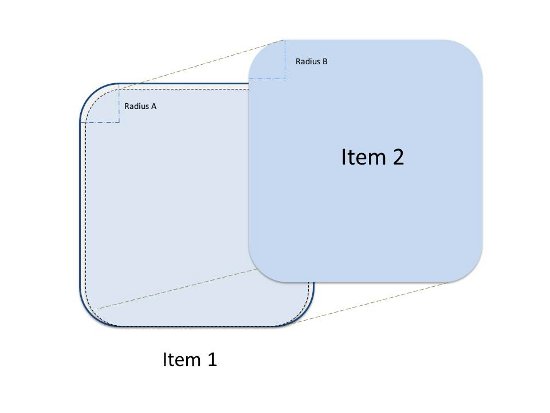
诡异的是理论上只要偏移量只要1dp就能显示1dp宽带边框了,但我在listview里实验了一下发现不行,换成2dp方可。有同学能解释解释么?
如果要给图形加上圆角,只需要给每个shape加上
1
2
3
| <corners
android:topLeftRadius="5.0dip"
android:topRightRadius="5.0dip" />
|
值得注意的是,两个shape的radius在设置的时候请确保前面的图层不会把后面的挡住。


