当利用 Scroller 去滑动屏幕或者扩展 ScrollView 的时候,总是会用到 getScrollX 和 getScrollY 去获取当前View 滑动到的位置,那么getScrollX() 和 getScrollY() 获取的到底是什么呢?
由于getScrollX 和 getScrollY 本质 上是一样的东西,下面只说明一下getScrollX, 一般是在屏幕上面左右划动的时候会去获取这个值。
请看下图:
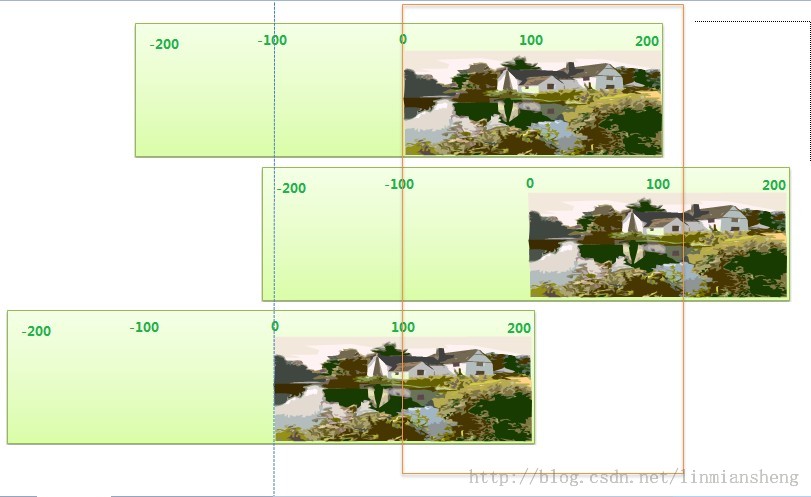
图上面,褐色的框,其实就是我们眼睛看到的手机界面,就是一个窗口。
而绿色的长方体呢,就是一块可以左右拉动的幕布啦,其实也就是我们要显示在窗口上面的内容,它其实是可以很大的,大到无限大,只是没在窗口中间的,所以我们就看不到。
而getScrollX 其实获取的值,就是这块 幕布在窗口左边界时候的值了,而幕布上面哪个点是原点(0,0)呢?就是初始化时内容显示的位置。
所以当我们将幕布往右推动的时候,幕布在窗口左边界的值就会在0的左边(-100),而向左推动,则其值会是在0的右边(100)。
下面以一个实际例子来看一下。
随便在CSDN上面截了一下图
我们在一个LinearLayout 里面定义了三个TextView 来显示 getScrollX() 的值,三个ImageView来显示图片, 都是指向同一张图片,布局如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#000000"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:textColor="#FFFFFF"
android:textSize="16sp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"/>
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/scrollImageView"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/scroll_testing"
android:contentDescription="Testing Scrolling"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textViewToRight"
android:textColor="#FFFFFF"
android:textSize="16sp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"/>
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/scrollImageViewToRight"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/scroll_testing"
android:contentDescription="Testing Scrolling"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textViewToLeft"
android:textColor="#FFFFFF"
android:textSize="16sp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"/>
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/scrollImageViewToLeft"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/scroll_testing"
android:contentDescription="Testing Scrolling"/>
</LinearLayout>
|
然后我们在Activity 中,分别对下面两张ImageView 进行 scrollTo 操作,然后获取其getScrollX() 的值,放到对应的TextView 上面,其代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| public class ScrollActivity extends Activity{
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState){
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.scroll_layout);
ImageView imageView = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.scrollImageView);
TextView textView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView);
textView.setText("getScrollX() = " + imageView.getScrollX());
ImageView imageViewToRight = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.scrollImageViewToRight);
imageViewToRight.scrollTo(-100, 0);
TextView textViewToRight = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textViewToRight);
textViewToRight.setText("getScrollX() = " + imageViewToRight.getScrollX());
ImageView imageViewToLeft = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.scrollImageViewToLeft);
imageViewToLeft.scrollTo(100, 0);
TextView textViewToLeft = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textViewToLeft);
textViewToLeft.setText("getScrollX() = " + imageViewToLeft.getScrollX());
}
}
|
下面是运行后的效果

可以看到,正如上面所说的,向右滚动的时候,等于是把背后的幕布向右推动,使得没有内容的幕布(X < 0)显示出来, 而向左滚动,则是把幕左向左推动,让右边的内容(X > 0)移到窗口的左边缘上。
在View上面还一个叫ScrollBy的函数,跟ScrollTo的区别在于,ScrollTo 是 到那个位置,ScrollBy 是经过这段位置,这个从英文的To 跟 By 来理解就很简单了。


